AGENT BASED
MODELING LABWelcome to the NYU Agent-Based Modeling Lab
We are NYU’s hub for research, courses, real-world applications, seminars, events, and projects on Agent-Based Modeling in public health and the social and behavioral sciences.
Artificial Societies and Generative Social Science
Agent-Based Models (ABMs) are artificial societies of software people (though agents can also be mosquitoes, viruses, vehicles, teams) who interact with one another to generate surprising and important social patterns of scientific and policy interest. Racial segregation, intergroup conflict, skewed distributions of wealth, pandemic spread, financial contagion, ancient civilizations, urban dynamics, social networks, and more have been generated “from the bottom up” in micro-worlds of agents. The method of agents positions us to understand how the micro world of individuals generates the macro world of collective phenomena. Indeed, the agent-based model is the principal scientific instrument in providing generative explanations for macro-patterns. The motto of this new “generative” social science is, “If you didn’t grow it, you didn’t explain it.” And we have grown a lot!
About the Lab
Like real people, these agents can be driven (often unawares) by powerful emotions; they may have poor information, and can make systematic errors interpreting it! One recent example is Epstein’s Agent_Zero. When multiple agents of this type interact directly in a computer, all sorts of important macroscopic phenomena can emerge--patterns of segregation, financial panics, collective violence, unhealthy behaviors. Indeed, to understand these, we generate--or “grow”--them from the bottom up in agent models. Epstein’s term for the approach is Generative Social Science.
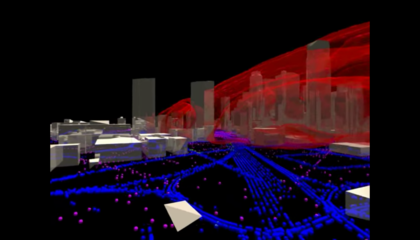
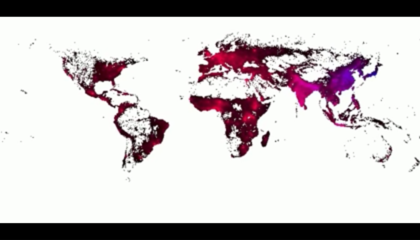
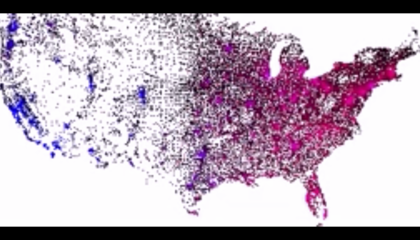
The agent-based technique has been applied to a vast array of phenomena, from epidemics to the distribution of wealth. Several of these models are shown below, in the Gallery of Models. Some are revealing “Toy” models (like the smallpox county-level model), while others are high fidelity models of Los Angeles, the United States, or the entire Planet.
Agent Based Modeling has been recognized as a “Transformative Innovation” by NIH, and has matured scientifically to the point that NYU is offering Undergraduate and Graduate curricula and a Certificate Program in this burgeoning field. The Lab is the hub for this unique and visionary NYU Initiative. To ensure that it encompasses the entire University, Epstein holds affiliated appointments in the Tandon School of Engineering, the School of Arts and Sciences, and the Courant Institute for Mathematical Sciences. All of these Schools are represented on the Advisory Board of the LAB (roster below), as is the Santa Fe Institute, where Epstein is an External Professor.
The essential mission of the Lab and its affiliates is to advance interdisciplinary science, deepening the theoretical foundations, and expanding the humane applications, of agent-based modeling and complementary areas of mathematics across the social, behavioral, and health sciences.
Selected Projects
NYC Urban Health Dynamics Simulator. Originally designed for Zika, but generalised to study a wide range of health issues, for STDs to Pandemic Flu.
Plume-Agent Model of Lower Manhattan and Resilience of Mega-Cities. This expands the Los Angeles Plume-Agent Model shown in the Gallery to New York City, as part of a large project on resilience of mega-cities worldwide.
Extending Agent_Zero. We are extending Epstein’s next-generation cognitive agent and populating our models with agents of this sort. They have emotions (like fear), bounded rationality, and are connected in social networks, producing collective behaviors in public health, economics, and civil violence. One extension is...
Addict-Zero, who we will use to study to study addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and opiates.
Shigellosis Model, with the NYC Department of Health
Cycles of Vigilance and Complacency in a model with competing fears. This can help explain cycles of vaccine refusal, voter turnout, yo-yo-dieting, and cycles of the 1918 pandemic.
Endogenous Inequality in Agent Populations. Related to the econophysics literature on Boltzmann economies and maximum entropy.
A Textbook on Agent-Based Modeling (to be offered online worldwide)
Ongoing research in the area of urban dynamics, scaling, and segregation with Geographical Information Systems
Theoretical work on Agents and Rational Choice, Robustness of Agent Models, and other foundational concerns.
Meet the Team
Leadership
Joshua Epstein (Director)
Erez Hatna (Associate Director)
Lecia Ductan (Administrator and Project Coordinator)
Harman Deep (RA and Student Activities)
Advisory Board
Cheryl Healton, DrPH, MPA
Dean, School of Global Public Health (GPH)
Professor of Public Health Policy and Management (GPH)
Rebecca Betensky, PhD
Chair and Professor of the Department of Biostatistics (GPH)
Katepalli “Sreeni” Sreenivasan, PhD, MEng
Former Dean, Tandon School of Engineering
Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Physics, and Mathematics (Tandon, Courant)
David Krakauer, PhD
President Santa Fe Institute
Ben Goldberg, PhD
Associate Professor of Computer Science (Courant)
Michael Laver, PhD
Former Dean, College of Arts and Sciences
Professor of Politics and co-director Center for Data Sciences (Courant)
Dan Stein, PhD, MSc
Professor of Physics and Mathematics (Courant)
External Faculty
Professor George Akerlof, Georgetown, Nobel Laureate in Economics
Professor Robert Axtell, George Mason, Santa Fe Institute, Oxford University
Professor Michael Batty, Center for Advanced Spatial Analysis, Kings College London
Professor Eric Beinhocker, Institute for New Economic Thinking at the Oxford Martin School, University of Oxford
Professor Itzhak Benenson, Tel Aviv University
Dr. Sebastian Benthall, Research Scientist, Information Law Institute, NYU
Professor Christopher Barrett, Director, Biocomplexity Institute, University of Virginia
Dr. Georgiy Bobashev, Biostatistics and Modeling, Research Triangle Institute
Professor Gerardo Chowell, Mathematical Epidemiology, Georgia State University
Professor Ian Cousin, Director Max Planck Institute Berlin, Evolutionary Ecology
Jennifer Crodelle, NSF Postdoctoral Fellow, Courant Institute
Professor Andrew Crooks, Geography and Computational Social Science, GMU
Professor Derek Cummings, Biology, University of Florida
Professor Doyne Farmer, Mathematics and New Economics Institute, Oxford University
Professor Duncan Foley, Economics, The New School and Santa Fe Institute
Professor Paul Glimcher, Neuroscience and Director ISDM, NYU
Professor Elodie Ghedin, Biology and Epidemiology, NYU
Professor Patrick Grim, Philosophy, Michigan University
Professor Peter Hedström, Institute for Analytical Sociology, Linköping University
Professor Dirk Helbing, ETH Zurich, Complex Systems Physics
Professor Wander Jager, Complex Systems, University of Groningen
Professor Ali Khan, Economics, Johns Hopkins
Professor Alan Kirman, Economics, Aix-en-Provence
Professor Tanya Liese, Mathematics, Amherst College
Professor Scott Page, Director of the Center for the Study of Complex Systems, Michigan
Professor Robin Purshouse, Decision Sciences, University of Sheffield
Professor Flaminio Squazzoni, Economic Sociology, University of Milan
Professor Brian Skyrms, Philosophy, UC Irvine
Professor Steven Strogatz, Applied Mathematics, Cornell University
Professor Gerard Weisbuch, Physics, Ecole Normale, Paris
Professor Lai-Sang Young, Mathematics, Courant Institute
Professor Peyton Young, Economics, Oxford University
Resources
Email: cgph.abmlab@nyu.edu
Twitter: @nyu_ABMLab
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/NYU-Agent-Based-Modeling-Lab-153803452091206/
Agent-Based Modeling: From Napkins to Nations [Watch Video]
Joshua Epstein on Contagion & Fear (Commonweal Magazine)
Are We Already Missing the Next Epidemic? (Politico)
EP90 Joshua Epstein on Agent-Based Modeling (The Jim Rutt Show)
Also featured on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
What Computer Models Show Us About Democracy (WNYC Studio)
Agent Zero and Generative Social Science
Agent Zero and Integrative Economics